HTTP 요청데이터
HTTP 요청 데이터 - 개요
HTTP 요청 메시지를 통해 클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전달하는 방법은
주로 다음 3가지 방법을 사용한다.
- GET - 쿼리 파라미터
- /url?username=hello&age=20 메시지 바디 없이, URL의 쿼리 파라미터에 데이터를 포함해서 전달
- 예) 검색, 필터, 페이징등에서 많이 사용하는 방식
- POST - HTML Form
- content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 메시지 바디에 쿼리 파리미터 형식으로 전달 username=hello&age=20
- 예) 회원 가입, 상품 주문, HTML Form 사용
- HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML, TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST, PUT, PATCH
1. HTTP 요청 데이터 - GET 쿼리 파라미터
System.out.println("[전체 파라미터 조회] - start")
request.getParameterNames().asIterator()
.forEachRemaining(paramName -> System.out.println(paramName + "=" + request.getParameter(paramName)));
System.out.println("[전체 파라미터 조회] - end");
System.out.println("[단일 파라미터 조회]");
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
System.out.println("username = " + username);
System.out.println("age = " + age);
System.out.println("[이름이 같은 복수 파라미터 조회]");
String[] usernames = request.getParameterValues("username");
for (String name : usernames) {
System.out.println("username = " + name);
}
2. HTTP 요청 데이터 - POST HTML Form
이번에는 HTML의 Form을 사용해서 클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전송해보자.
주로 회원 가입, 상품 주문 등에서 사용하는 방식이다.
특징
content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
메시지 바디에 쿼리 파리미터 형식으로 데이터를 전달한다. username=hello&age=20
application/x-www-form-urlencoded 형식은 앞서 GET에서 살펴본 쿼리 파라미터 형식과 같다.
따라서 쿼리 파라미터 조회 메서드를 그대로 사용하면 된다.
클라이언트(웹 브라우저) 입장에서는 두 방식에 차이가 있지만, 서버 입장에서는 둘의 형식이 동일하므로, request.getParameter() 로 편리하게 구분없이 조회할 수 있다.
정리하면 request.getParameter() 는 GET URL 쿼리 파라미터 형식도 지원하고, POST HTML Form 형식도 둘 다 지원한다.
Postman을 사용한 테스트
이런 간단한 테스트에 HTML form을 만들기는 귀찮다. 이때는 Postman을 사용하면 된다.
- Body x-www-form-urlencoded 선택
- Headers에서 content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
3. HTTP 요청 데이터 - API 메시지 바디 - 단순 텍스트
- HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML, TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST, PUT, PATCH
@WebServlet(name = "requestBodyStringServlet", urlPatterns = "/request-body-string")
public class RequestBodyStringServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("messageBody = " + messageBody);
response.getWriter().write("ok");
}
}
Postman을 사용하여 테스트
- POST http://localhost:8080/request-body-string
- content-type: text/plain
- message body: hello
- 결과: messageBody = hello
3. HTTP 요청 데이터 - API 메시지 바디 - JSON
이번에는 HTTP API에서 주로 사용하는 JSON 형식으로 데이터를 전달해보자.
json 받을 객체를 위해 HelloData 클래스 생성해야함.
@WebServlet(name = "requestBodyJsonServlet", urlPatterns = "/request-body-json")
public class RequestBodyJsonServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("messageBody = " + messageBody);
HelloData helloData = objectMapper.readValue(messageBody, HelloData.class);
System.out.println("helloData.username = " + helloData.getUsername());
System.out.println("helloData.age = " + helloData.getAge());
response.getWriter().write("ok");
}
}Postman을 사용하여 JSON 형식 전송
- POST http://localhost:8080/request-body-json
- content-type: application/json
- message body: {"username": "hello", "age": 20}
- 결과: messageBody = {"username": "hello", "age": 20}
HTTP 응답 데이터
HtpServletResponse - 기본 사용법
HttpServletResponse 역할
- HTTP 응답 메시지 생성
- HTTP 응답코드 지정
- 헤더 생성
- 바디 생성
편의 기능 제공
- Content-Type, 쿠키, Redirect
@WebServlet(name = "responseHeaderServlet", urlPatterns = "/response-header")
public class ResponseHeaderServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//[status-line]
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK); // = 200
//[response-headers]
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain");
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache, no-store, must-revallidate");
response.setHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");
response.setHeader("my-header", "hello");
response.getWriter().write("ok");
}
}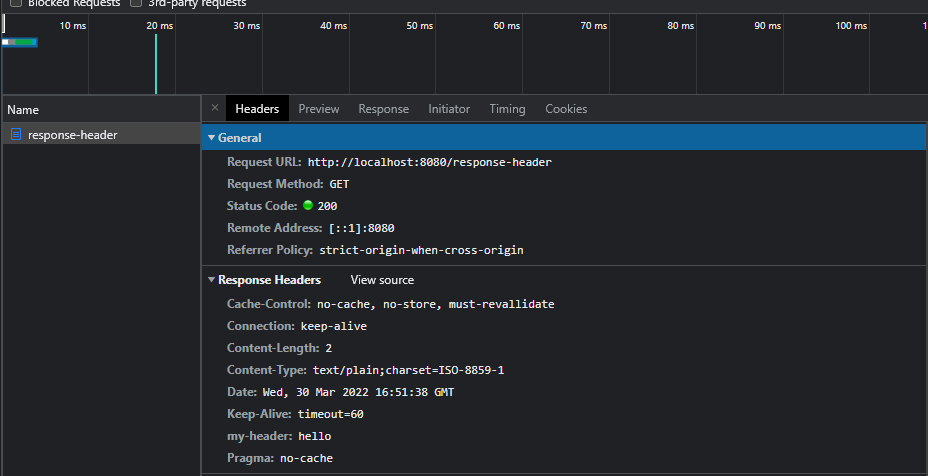
위에서 작성한 정보들이 Header로 보내진다.
이 외에
Content 편의 메서드
쿠키 편의 메서드
redirect 편의 메서드가 있다.
HTTP 응답 데이터 - 단순 텍스트, HTML
HTTP 응답 메시지는 주로 다음 내용을 담아서 전달한다.
- 단순 텍스트 응답
- 앞에서 살펴봄 ( writer.println("ok"); )
- HTML 응답
- HTTP API - MessageBody JSON 응답
HTTP 응답으로 HTML을 반환할 때는 content-type을 text/html 로 지정해야 한다.
HTTP 응답 데이터 - API JSON
@WebServlet(name = "responseJsonServlet", urlPatterns = "/response-json")
public class ResponseJsonServlet extends HttpServlet {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Content-Type: application/json
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
HelloData helloData = new HelloData();
helloData.setUsername("kim");
helloData.setAge(20);
//{"username":"kim", "age":20}
String result = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(helloData);
response.getWriter().write(result);
}
}
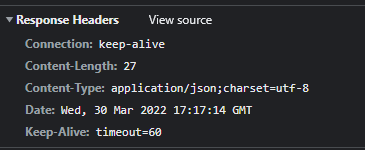
HTTP 응답으로 JSON을 반환할 때는 content-type을 application/json 로 지정해야 한다.
Jackson 라이브러리가 제공하는 objectMapper.writeValueAsString() 를 사용하면 객체를 JSON 문자로 변경할 수 있다.
인프런 김영한님의 스프링 MVC 1편을 듣고 작성한 글입니다.
스프링 MVC 1편 - 백엔드 웹 개발 핵심 기술 - 인프런 | 강의
웹 애플리케이션을 개발할 때 필요한 모든 웹 기술을 기초부터 이해하고, 완성할 수 있습니다. 스프링 MVC의 핵심 원리와 구조를 이해하고, 더 깊이있는 백엔드 개발자로 성장할 수 있습니다., -
www.inflearn.com
'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| MVC 패턴의 장점과 단점, 한계 (0) | 2022.04.02 |
|---|---|
| 서블릿, JSP 으로 회원관리 웹 만들기 (0) | 2022.04.01 |
| HttpServlet 기본 사용법 (0) | 2022.03.29 |
| 서블릿 프로젝트 시작 (0) | 2022.03.29 |
| 웹 애플리케이션 이해 (0) | 2022.03.28 |




댓글